Chocolate Spot Disease of Faba Bean
Faba bean is also known as broad bean, is one of the
earliest domesticated food legumes in the world, probably in the late Neolithic
period. Cultivated faba bean is mainly used as human food in developing
countries and animal feed in industrialized countries.
Chocolate spot is the most important
disease of faba beans. This disease can be managed through an integrated
approach including careful paddock selection, the use of resistant varieties
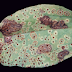
and strategic use of foliar fungicides. Symptoms are varied and range from
small spots on the leaves to complete blackening of the entire plant. Leaves
are the main part of the plant affected but under favorable conditions for the
disease, it also spreads to stems, flowers and pods.
Chocolate
spot, caused by Botrytis fabae and Botrytis cinerea, can survive either as
sclerotic in the soil or on crop debris, in infected seed, or plants.
Previously unaffected areas the disease developed by the sowing of infected
seed. Initially infection usually occurs when spores formed on old bean trash
are carried by wind into new crops. These spores may move long distances. Once
the disease becomes established it rapidly spreads within a crop, and within
4-5 days, the infection spores can be formed on infected tissue and spread the
disease throughout the plant.
The fungus is most aggressive it
occurs mainly under cool, humid conditions, particularly at flowering time.
Environmental conditions mainly determine the severity of a chocolate spot
disease. The optimum conditions are temperatures between 15 and 22°C with at
least 90 per cent relative humidity.
The above Article originally got
published at SciFed Journal of Mycology in 2017,To have a glance please visit: Click Here
.png)



0 comments: